Connect With Us

Wound Care
Diabetics must be wary of all wounds, regardless of depth or size. Diabetes, a chronic disease in which the body cannot properly use glucose the way it normally would, causes various complications that make wounds difficult to heal. Nerve damage or neuropathy will cause diabetics to have trouble feeling the pain of a blister or cut until the condition has significantly worsened or become infected. A diabetic’s weakened immune system can make even the most minor of wounds easily susceptible to infection. Diabetics are also more prone to developing narrow, clogged arteries, and are therefore more likely to develop wounds.
Wounds should be taken care of immediately after discovery, as even the smallest of wounds can become infected if enough bacteria build up within the wound. To remove dirt, wounds should be first rinsed under running water only. Soap, hydrogen peroxide, or iodine can irritate the injury and should be avoided. To prevent infection, apply antibiotic ointment to the wound and cover it with a bandage. The bandage should be changed daily. The skin around the wound may be cleaned with soap.
To prevent further exacerbation, see a doctor—especially if you have diabetes. Minor skin conditions can become larger problems if not properly inspected. As the wound heals, make sure to avoid applying pressure to the affected area.
Exercise for Your Feet
Whether your feet are over-worked or under-worked, chances are they could benefit from some special attention. Even those who exercise regularly probably do not spend any time strengthening their feet. This can be just as rewarding as strengthening the rest of the body, since the health of your feet affects the health of the rest of the body as well, especially the ankles, legs, and spine.
For those who might not have any idea on how a foot-specific exercise might be conducted, there are several workouts that are fairly easy to perform in the comfort of ones’ home. One of the easiest is the toe rise, also known as the tip-toe. This exercise involves standing on the tip-toes for a count of 15 then resting the feet on the ground. This process should be repeated a minimum of three times a day in order to strengthen the feet.
Toe pick-ups strengthen the feet by working them in a very different way. In this exercise, small items are picked up using the toes in order to strengthen the muscles on the upper part of the feet. Once again three sets should be performed, with the item in question being held for 15 seconds then dropped. Items that may be picked up using the feet include marbles and even stationery, which works wonders for the toes and the surrounding muscles.
Yet another simple workout is the ankle pump. This can be done either upwards or downwards, but for the workout to be most effective both can be incorporated into the routine. As the term suggests, this involves lifting the foot off the floor and flexing the toes either towards the shin or towards the ground. This movement puts the feet and ankles through a large range of motion which works the muscles.
Last but not least, feet should be stretched so that the muscles can relax and recuperate. This can be done by placing both feet off of the floor and bracing oneself against the wall at a 45 degree angle. This ensures that the feet and ankles are adequately stretched once the workout is complete.
In short, giving the feet a good workout every now and then is important in order to avoid problems such as plantar fasciitis. It’s also important to warm-up or cool-down after running or vigorous walking. Foot exercises may be followed by a good foot massage. This encourages circulation in the feet as well as muscle relaxation.
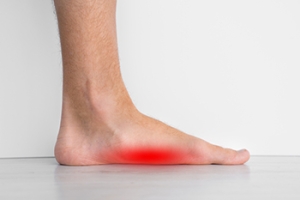
What Can Provide Relief for Patients Who Have Pain From Flat Feet?
The medical name for flat feet is called pes planus. Flat feet are noticeable while standing on the floor, as the entire foot lies flat. There are some patients who have a small arch, and this is considered to be in the flat foot family. Babies are born with flat feet, and the arch generally develops between ages three and six. This happens as a result of the baby’s foot outgrowing the fat pad, and balance is often improved. If the arch fails to develop, it may be because of tight calf muscles, flexible foot and ankle ligaments, and generally poor foot stability. Many patients have little pain with flat feet, and specific stretches may help to improve flexibility. If there is pain and discomfort from this condition and completing daily activities becomes difficult to accomplish, it is suggested that you confer with a podiatrist who can prescribe custom-made orthotics, and help you with correct exercises and stretches that may provide relief.
Flatfoot is a condition many people suffer from. If you have flat feet, contact Dr. Michael D. Garvin from Florida. Our doctor will treat your foot and ankle needs.
What Are Flat Feet?
Flatfoot is a condition in which the arch of the foot is depressed and the sole of the foot is almost completely in contact with the ground. About 20-30% of the population generally has flat feet because their arches never formed during growth.
Conditions & Problems:
Having flat feet makes it difficult to run or walk because of the stress placed on the ankles.
Alignment – The general alignment of your legs can be disrupted, because the ankles move inward which can cause major discomfort.
Knees – If you have complications with your knees, flat feet can be a contributor to arthritis in that area.
Symptoms
- Pain around the heel or arch area
- Trouble standing on the tip toe
- Swelling around the inside of the ankle
- Flat look to one or both feet
- Having your shoes feel uneven when worn
Treatment
If you are experiencing pain and stress on the foot you may weaken the posterior tibial tendon, which runs around the inside of the ankle.
If you have any questions please feel free to contact our offices located in Port St. Lucie, FL . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot and ankle needs.
What is Flexible Flat Foot?
Flatfoot is classified as having the entire sole of the foot in contact or near contact to the ground while standing. The disorder is also known as fallen arches, because those affected have no arch in their feet. Flexible flatfoot and rigid flatfoot are the two types of flatfoot.
A person has flexible flatfoot if when sitting or standing on their toes, they have an arch that disappears when they stand with the entire foot on the ground. Flexible flatfoot may also be called “pediatric flatfoot” because the condition first appears in childhood. It is common among infants because the arch does not develop until the age of 5 or 6 years. Rigid flatfoot is not as common in children as it is with adults. This type of flatfoot is developed due to the weakening of tibialis posterior muscle tendon, a major supporting structure of the foot arch. Development of this deformity is progressive and shows early signs of pain and swelling that begins at the inside arch of the foot and moves to the outside of the foot below the ankle. More severe cases can possibly lead to arthritis of the foot and ankle joints.
Although most cases of flatfoot involve people born with the condition, some less common causes are obesity, diabetes, pregnancy, and osteoporosis. In some cases, flatfoot may come with no symptoms at all and does not require any type of treatment. With other cases though, symptoms may include pain in the shin, knee, hips and lower back. If a person with flatfeet experiences such symptoms, a health care provider may suggest using orthotic devices or arch supports, which may reduce the pain. Wearing supportive shoes can also prove more comfortable with flatfeet and staying away from shoes with little support such as sandals. Other methods to relieve pain also include stretching the Achilles tendon properly and using proper form when doing any physical activity. In addition, losing weight can reduce the stress on your feet and reduce the pain.
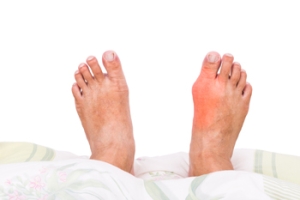
What Is Causing My Painful Bunion?
 Bunions are a very common foot condition that cause a bony lump to form at the main joint of the big toe. This occurs when the joint is pulled out of alignment because the big toe is turned towards the rest of the toes. While bunions may not cause pain or symptoms at first, they can eventually push the other toes out of alignment making it difficult to wear shoes or walk. Bunions even have a tendency of causing skin irritation as the shoes rub against the affected area. Bunions can be caused due to inherited defects in the foot structure, wearing poorly fitted shoes, arthritis, conditions that damage the nerves in the feet, and of course injuries. If you are suffering from a painful bunion, consulting with a podiatrist for pain relief methods is highly suggested.
Bunions are a very common foot condition that cause a bony lump to form at the main joint of the big toe. This occurs when the joint is pulled out of alignment because the big toe is turned towards the rest of the toes. While bunions may not cause pain or symptoms at first, they can eventually push the other toes out of alignment making it difficult to wear shoes or walk. Bunions even have a tendency of causing skin irritation as the shoes rub against the affected area. Bunions can be caused due to inherited defects in the foot structure, wearing poorly fitted shoes, arthritis, conditions that damage the nerves in the feet, and of course injuries. If you are suffering from a painful bunion, consulting with a podiatrist for pain relief methods is highly suggested.
If you are suffering from bunions, contact Dr. Michael D. Garvin of Florida. Our doctor can provide the care you need to keep you pain-free and on your feet.
What Is a Bunion?
A bunion is formed of swollen tissue or an enlargement of boney growth, usually located at the base joint of the toe that connects to the foot. The swelling occurs due to the bones in the big toe shifting inward, which impacts the other toes of the foot. This causes the area around the base of the big toe to become inflamed and painful.
Why Do Bunions Form?
Genetics – Susceptibility to bunions are often hereditary
Stress on the feet – Poorly fitted and uncomfortable footwear that places stress on feet, such as heels, can worsen existing bunions
How Are Bunions Diagnosed?
Doctors often perform two tests – blood tests and x-rays – when trying to diagnose bunions, especially in the early stages of development. Blood tests help determine if the foot pain is being caused by something else, such as arthritis, while x-rays provide a clear picture of your bone structure to your doctor.
How Are Bunions Treated?
- Refrain from wearing heels or similar shoes that cause discomfort
- Select wider shoes that can provide more comfort and reduce pain
- Anti-inflammatory and pain management drugs
- Orthotics or foot inserts
- Surgery
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our offices located in Port St. Lucie, FL . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
What Are Bunions?
Bunions are large bony bumps at the base of the big toe. Medically known as hallux valgus, a bunion is a misalignment of the metatarsophalangeal joint, or big toe joint. The misalignment will generally worsen with time if left untreated.
The exact cause of bunions is unknown, with genetics seen as a potential cause. High heels and poorly-fitted footwear, rheumatoid arthritis, and heredity all seem to be potential factors behind the exacerbation of bunions. Women have been found to be more likely to develop bunions in comparison to men.
Bunions do not always produce symptoms. The best way to tell is if the big toe is pushing up against the next toe and there is a large protrusion at the base of the big toe. You may or may not feel pain. Redness, swelling, and restricted movement of the big toe may be present as well.
Podiatrists use a variety of methods to diagnose bunions. If there are symptoms present, podiatrists will first consider that it is a bunion. If not, a physical examination will be conducted to check function of the big toe. Finally, an X-ray may be taken to view the extent of the bunion and confirm it is a bunion.
Typically, nonsurgical methods are used to treat bunions, unless the bunion has become too misaligned. Orthotics, icing and resting the foot, roomier and better fitted shoes, taping the foot, and pain medication are usually utilized first. If the bunion doesn’t go away or causes extreme pain, surgery may be required. Surgeons will either remove part of the swollen tissue or bone to straighten the toe out.
If you have a bunion, it is recommended to see a podiatrist. The longer it is left untreated, the worse it may get. Podiatrists can properly diagnose and treat a bunion before it gets worse.
What Is a Ringworm Infection?
Despite the creepy-crawly implications of its name, ringworm is actually not a worm at all, but rather a fungal infection. The name ringworm comes from the red, scaly, itchy, ring-shaped rash that appears on infected skin. This type of infection often affects the feet and is commonly referred to as “athlete’s foot.” The rash associated with athlete’s foot can affect any part of the foot, but is usually found in between the toes or on the soles of the feet. It is highly contagious and can easily spread to other people or other parts of the body. Athlete’s foot can be treated through topical or oral antifungal medications. If you have a red, scaly rash on your feet, it is suggested that you seek the care of a podiatrist.
Athlete’s Foot
Athlete’s foot is often an uncomfortable condition to experience. Thankfully, podiatrists specialize in treating athlete’s foot and offer the best treatment options. If you have any questions about athlete’s foot, consult with Dr. Michael D. Garvin from Florida. Our doctor will assess your condition and provide you with quality treatment.
What Is Athlete’s Foot?
Tinea pedis, more commonly known as athlete’s foot, is a non-serious and common fungal infection of the foot. Athlete’s foot is contagious and can be contracted by touching someone who has it or infected surfaces. The most common places contaminated by it are public showers, locker rooms, and swimming pools. Once contracted, it grows on feet that are left inside moist, dark, and warm shoes and socks.
Prevention
The most effective ways to prevent athlete’s foot include:
- Thoroughly washing and drying feet
- Avoid going barefoot in locker rooms and public showers
- Using shower shoes in public showers
- Wearing socks that allow the feet to breathe
- Changing socks and shoes frequently if you sweat a lot
Symptoms
Athlete’s foot initially occurs as a rash between the toes. However, if left undiagnosed, it can spread to the sides and bottom of the feet, toenails, and if touched by hand, the hands themselves. Symptoms include:
- Redness
- Burning
- Itching
- Scaly and peeling skin
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis is quick and easy. Skin samples will be taken and either viewed under a microscope or sent to a lab for testing. Sometimes, a podiatrist can diagnose it based on simply looking at it. Once confirmed, treatment options include oral and topical antifungal medications.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact our offices located in Port St. Lucie, FL . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot care needs.
Athlete's Foot
Athlete’s foot is an extremely contagious infection caused by a fungus that results in itching, burning, dry, and flaking feet. The fungus that causes athlete’s foot is known as tinea pedis and thrives in moist, dark areas such as shower floors, gyms, socks and shoes, commons areas, public changing areas, bathrooms, dormitory style houses, locker rooms, and public swimming pools. Athlete’s foot is difficult to treat as well because of the highly contagious and recurrent nature of the fungus.
Tinea is the same fungus that causes ringworm, and is spread by direct contact with an infected body part, contaminated clothing, or by touching other objects and body parts that have been exposed to the fungus. Because the feet are an ideal place for tinea to grow and spread, this is the most commonly affected area. It is, however, known to grow in other places. The term athlete’s foot describes tinea that grows strictly on the feet.
The most commonly infected body parts are the hands, groin, and scalp, as well as the feet. Around 70% of the population suffer from tinea infections at some point in their lives, however not all of these cases are athlete’s foot. Just like any other ailment, some people are more likely to get it than others, such as people with a history of tinea infections or other skin infections, both recurring and non-recurring ones. The extent to which a person experiences regrowth and recurrent tinea infections varies from person to person.
Sometimes people will not even know that they are infected with tinea or that they have athlete’s foot because of a lack of symptoms. However, most experience mild to moderate flaking, itching, redness, and burning. However, some of the more severe symptoms include cracking and bleeding skin, intense itching and burning, pain while walking or standing, and even blistering.
Because of the recurring nature of the tinea fungus and the athlete’s foot it causes, the best way to treat this condition is with prevention. You can take some preventative measures such as wearing flip flops or sandals in locker rooms and public showers to reduce contact with the floor. It also helps to keep clean, dry feet while allowing them to breathe. Using powders to keep your feet dry is a good idea, as well as keeping your feet exposed to light and cool air, to prevent the growth of tinea. If you do happen to get athlete’s foot, opt for using topical medicated creams, ointments or sprays. These treatments help eliminate and prevent it from coming back.
What Are Sesamoids?
The sesamoid bones are located in the ball of the foot, just behind the big toe. These two tiny pea-sized bones support tendons in the feet and allow downward motion of the big toe. When the sesamoids are inflamed it is known as sesamoiditis. This condition usually arises as a result of a sudden injury that bends the big toe upwards. People who participate in sports that put stress on the sesamoid bones, such as football, soccer, and dance, are at an increased risk of sesamoid injuries. Suddenly increasing the intensity of your workouts or wearing ill-fitted shoes or shoes with excessively high heels can also make sesamoiditis more likely. Symptoms of this condition include pain under the ball of the foot, a restricted range of motion in the big toe, and a popping sensation in your big toe when you walk. If you suspect that you may have sesamoiditis, please seek the care of a podiatrist.
Sesamoiditis is an unpleasant foot condition characterized by pain in the balls of the feet. If you think you’re struggling with sesamoiditis, contact Dr. Michael D. Garvin of Florida. Our doctor will treat your condition thoroughly and effectively.
Sesamoiditis
Sesamoiditis is a condition of the foot that affects the ball of the foot. It is more common in younger people than it is in older people. It can also occur with people who have begun a new exercise program, since their bodies are adjusting to the new physical regimen. Pain may also be caused by the inflammation of tendons surrounding the bones. It is important to seek treatment in its early stages because if you ignore the pain, this condition can lead to more serious problems such as severe irritation and bone fractures.
Causes of Sesamoiditis
- Sudden increase in activity
- Increase in physically strenuous movement without a proper warm up or build up
- Foot structure: those who have smaller, bonier feet or those with a high arch may be more susceptible
Treatment for sesamoiditis is non-invasive and simple. Doctors may recommend a strict rest period where the patient forgoes most physical activity. This will help give the patient time to heal their feet through limited activity. For serious cases, it is best to speak with your doctor to determine a treatment option that will help your specific needs.
If you have any questions please feel free to contact our offices located in Port St. Lucie, FL . We offer the newest diagnostic and treatment technologies for all your foot and ankle needs.
Sesamoiditis
Sesamoiditis is a condition that affects the joint that is just behind the big toe in the area known as the ball of the foot. It is most common in younger people and people who have just begun an exercise program. Since the sesamoid bones are like a pulley controlling the big toe, they can rub against each other and cause a gradual onset of pain. Pain may also be caused by the inflammation of tendons surrounding the bones. If ignored, sesamoiditis can lead to other, more serious problems such as severe irritation and fractures of the bones.
The cause of sesamoiditis is sudden increase in activity. The ball of your foot acts as a springboard to help you lift off when you are jogging or running. Sudden increase in the use of these bones or the tendon that controls them can cause irritation. The tendon then begins to develop inflammation and the joint begins to swell. People with smaller, bonier feet or those with a high arch are typically more susceptible to this condition.
Sesamoiditis is fairly simple to diagnose since the symptoms have a gradual onset rather than a sudden impact. The symptoms begin with slight irritation around the joint shortly after the increase in activity. The discomfort eventually turns to pain with light swelling and possibly redness. Although redness or bruising are rare, this may be a symptom. After each session of exercising, the aggravated joint becomes more irritated and increases into a very intense throbbing.
Treatment for sesamoiditis can vary depending on the severity of the situation. However, treatment is almost always approached in a noninvasive way. For a case that is just beginning the doctor may recommend a very strict rest period that will limit the activity allowed on the joint. If you must be active, a recommendation for as modified shoe or insole, along with bandaging and immobilizing the big toe will be made to ensure that pressure is not placed on the joint. For severe cases, it is typically recommended that the joint and the big toe be completely immobilized to allow adequate time to heal. Ice and an over the counter anti-inflammatory may can help with the pain and discomfort while you are at rest.
When you return to your regular exercise activities, it is recommended that you use an insole that will allow even distribution of impact to your entire foot, rather than just the balls of your foot. This will prevent further aggravation of the injury.